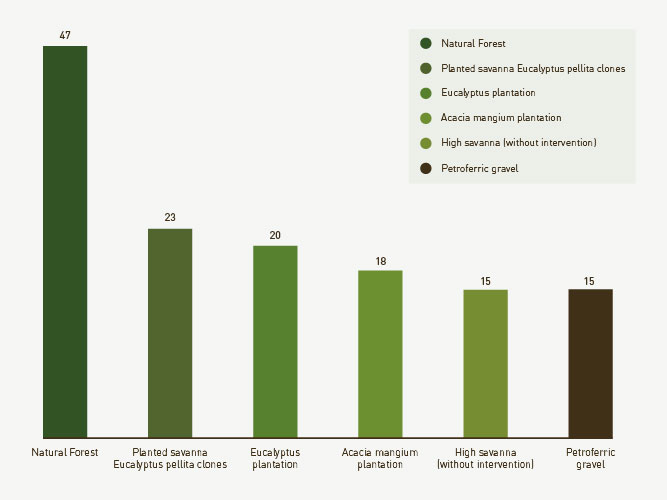
The unique biodiversity of Vichada stimulates the need to enhance the understanding of the genetic complexity of its ecosystems. As part of an initiative aimed at investigating the contribution and dynamics of biological diversity, we have elaborated a study that focuses on identifying the variety of life forms associated with soils subjected to different types of cover. In addition, it analyzes the possible impact of planted forests on soil biodiversity, especially in savannas that have historically suffered from degradation processes.
InverBosques, in alliance with Nature Metrics, has conducted a research study on soil DNA that provides us with fundamental knowledge for the efficient management and conservation of the invaluable biological diversity present in the region. This study enables the identification of hidden soil biodiversity, the detection of new and unknown species, the analysis of the specific functions of these ecosystems, and valuable information for the conservation and sustainable management of soils in the area.
A single gram of soil can host hundreds of species of bacteria, fungi and microscopic animals. This little-known world of biodiversity plays a critical role in the support of healthy ecosystems, ranging from forests to farmland.
To conduct the baseline study, a total of 50 soil samples were collected from a variety of habitats within our project’s area of influence. These samples represented a wide range of environments, providing a meaningful representation of the diversity of soils found in the region.